Examining the impact of economic factors on token distribution and supply in blur
Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto

Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto
In recent years, digital currencies have gained significant popularity and have revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with money. One such digital currency is Blur, a blockchain-based payment system that aims to provide users with fast, secure, and private transactions.
Token distribution and supply play a crucial role in the success and sustainability of any digital currency, including Blur. Understanding the economic factors that influence token distribution and supply is essential for investors, users, and developers alike. This article explores the key factors that affect token distribution and supply in Blur, highlighting their impact on the overall ecosystem.
One of the fundamental economic factors shaping token distribution in Blur is the initial coin offering (ICO) process. ICOs serve as a means for projects to raise funds in exchange for their token. The distribution of tokens during the ICO phase determines the initial supply available in the market. The success of an ICO depends on various factors, such as the project's credibility, the token economics, and the overall market sentiment towards the project. Developers must carefully plan the token distribution during the ICO to ensure a fair and balanced supply.
Another critical factor influencing token distribution and supply in Blur is the concept of token vesting. Token vesting refers to a mechanism where tokens are gradually released to investors or team members over a specified period. This measure helps prevent market manipulation and ensures a steady supply of tokens in circulation. Properly designed token vesting schedules can incentivize long-term commitment, align the interests of all stakeholders, and maintain a healthy market equilibrium.
In addition to ICOs and token vesting, the overall demand and adoption of Blur also play a significant role in token distribution and supply. As more individuals and businesses start using Blur for various transactions, the demand for tokens increases. Developers must monitor the demand closely and adjust the token supply accordingly to maintain stability in the market. The scarcity or abundance of tokens can greatly impact their value and the overall economic health of the Blur ecosystem.
In conclusion, token distribution and supply in Blur are influenced by various economic factors, including the ICO process, token vesting, and overall demand and adoption. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring a fair and balanced distribution of tokens, maintaining market stability, and fostering the growth of this innovative digital currency.
Economic Factors Affecting Token Distribution

The distribution of tokens in the blur.io ecosystem is influenced by various economic factors. These factors play a crucial role in determining the supply and availability of tokens to users within the platform. Understanding these factors is essential for users who want to participate in the blur.io ecosystem effectively.
Token Allocation

Token allocation is one of the primary economic factors affecting token distribution. The initial allocation of tokens is determined by the project team or organization behind blur.io. They decide how many tokens will be minted and how they will be distributed. Different projects may have different allocation strategies, such as a percentage allocated to the team, investors, or airdrops to the community.
Blur.io has a fair token distribution model that aims to provide equal opportunities for users to acquire tokens. The project team allocates a portion of tokens to be distributed through airdrops, ensuring wider access to tokens for community members.
Market Demand

Market demand is another crucial factor that influences token distribution. The more users and investors are interested in blur.io, the higher the demand for tokens becomes. High demand can lead to scarcity of tokens, driving up their price and making them more difficult to obtain.
Additionally, market demand affects the price of tokens on exchanges. Higher demand for a token generally results in an increase in its value. This can impact the distribution of tokens as some users may choose to hold onto their tokens instead of selling them, leading to a reduction in the available supply.
Token Utility
The utility of tokens within the blur.io ecosystem also plays a role in their distribution. Tokens may have various uses, such as accessing premium features, participating in voting, or purchasing exclusive content. The more utility a token has, the higher the demand becomes, potentially affecting distribution.
Token holders who see value in the utility of tokens are more likely to acquire and hold them, reducing the available supply for distribution. This can create a more concentrated distribution where a smaller number of holders control a significant portion of the token supply.
Overall, economic factors such as token allocation, market demand, and token utility have a significant impact on the distribution of tokens within the blur.io ecosystem. Understanding how these factors interact can help users navigate the platform and make informed decisions about token acquisition and usage.
To learn more about token distribution and how to sign up for blur.io, visit WIE MAN SICH BEI BLUR.IO ANMELDET.
Token Distribution Strategies
Token distribution is a crucial aspect of any token-based project, as it determines the initial supply of tokens and how they are allocated among various stakeholders. A well-designed token distribution strategy can help ensure the long-term sustainability and success of the project.
There are several token distribution strategies that a project can employ, depending on its specific goals and objectives. Some common strategies include:
Initial Coin Offering (ICO): In an ICO, the project team sells a portion of the total token supply to the public in exchange for another cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. This strategy allows the project to raise funds and distribute tokens to a wide range of investors.
Airdrops: Airdrops involve distributing tokens for free to a large number of wallet holders. This strategy is often used to create widespread awareness and build a community around the project. Airdrops can be targeted to specific groups or done on a first-come, first-served basis.
Bounty Programs: Bounty programs incentivize individuals to perform specific tasks, such as marketing, development, or bug reporting, in exchange for tokens. This strategy helps the project tap into the expertise and resources of the community and encourages active participation.
Private Sales: Private sales involve selling tokens to a select group of investors, typically institutional or high-net-worth individuals. This strategy allows the project to secure funding quickly and often at a higher price.
Community Allocation: Some projects allocate a portion of the token supply directly to the community. This can be done through community votes or other decentralized governance mechanisms, ensuring that stakeholders have a say in the project's development and future direction.
It is important for a project to carefully consider its token distribution strategy to ensure fairness, inclusivity, and alignment with its overall vision. A well-thought-out strategy can help attract a diverse set of stakeholders and foster a vibrant ecosystem around the project.
If you want to learn more about token distribution and supply in the blur ecosystem, you can explore the features and advantages of Blur.io. It provides a comprehensive platform for buying, selling, and trading tokens, ensuring a seamless and secure experience for users.
Economic Factors Affecting Token Supply
When analyzing token distribution and supply within the context of blur, there are several economic factors that come into play. These factors can significantly impact the overall availability and value of tokens within the blur ecosystem.
1. Token Demand: One of the primary drivers of token supply is the demand for the token. If there is high demand for the token, the supply may be limited in order to maintain its value. On the other hand, if the demand is low, the token supply may increase to encourage more usage and adoption.
2. Token Utility: The utility provided by the token also affects its supply. If the token has a wide range of use cases and provides significant value to users, it is more likely to have higher demand and a limited supply. Conversely, if the token has limited utility or does not offer substantial benefits, its supply may be more abundant.
3. Token Distribution Mechanism: The way tokens are distributed can also impact the overall token supply. For example, if tokens are airdropped to a large number of individuals, the supply may be higher compared to a situation where tokens are exclusively sold through a limited number of channels.
4. Token Burn Mechanism: Token burn refers to the deliberate and permanent destruction of tokens. This mechanism is often used to reduce token supply and increase its value. By reducing the total number of tokens in circulation, token burn can create scarcity and increase demand.
5. Inflation Rate: The inflation rate of tokens within a blockchain ecosystem can affect the supply. A higher inflation rate means more tokens are being added to circulation, potentially reducing their value. On the other hand, a lower inflation rate can create scarcity and increase token value.
6. External Factors: External economic factors, such as market conditions, regulatory changes, and investor sentiment, can also influence token supply. These factors can lead to fluctuations in token demand and supply, impacting the overall token economy.
Overall, the economic factors affecting token supply in blur are multifaceted. Token demand, utility, distribution mechanisms, burn mechanisms, inflation rate, and external factors all play a role in shaping the availability and value of tokens within the ecosystem.
Supply and Demand Dynamics in Token Economics
In the world of token economics, the interaction between supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining the value and distribution of tokens. Understanding these dynamics is essential for both investors and token issuers.
The supply of tokens refers to the total number of tokens available in the market. This supply can be fixed or elastic, depending on the design of the token. Fixed supply tokens have a predetermined number of tokens that cannot be changed. On the other hand, elastic supply tokens can adjust their total supply based on certain conditions or rules.
Token demand, on the other hand, represents the desire and willingness of individuals to acquire and hold tokens. Demand can be influenced by various factors, such as the token's utility, market trends, and investor sentiment. High demand for a token typically leads to an increase in its value, while low demand can result in a decrease.
The interaction between supply and demand determines the token's equilibrium price, which is the price at which the quantity of tokens demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. If the demand for tokens exceeds the supply, the price tends to rise. Conversely, if the supply exceeds the demand, the price tends to fall.
Token issuers can influence the supply and demand dynamics through various mechanisms. For instance, they can control the total supply of tokens through initial coin offerings (ICOs), token burns, or token minting. Additionally, token issuers can drive demand by creating strong use cases for the token, partnerships with other projects, or by ensuring liquidity on exchanges.
Investors, on the other hand, need to analyze the supply and demand dynamics to make informed decisions. They need to consider factors such as the token's total supply, distribution mechanism, and the potential demand for the token in the future.
In conclusion, the supply and demand dynamics in token economics are crucial in determining token value and distribution. Token issuers and investors should closely monitor these dynamics and consider them when making decisions in the token market.
Economic Incentives for Token Holders
Token holders play a crucial role in the success and growth of a blockchain project. Therefore, it is essential to create economic incentives that encourage holders to actively participate in the network and maintain the stability of the token supply.
One of the primary economic incentives for token holders is the potential for financial rewards. Many blockchain projects implement mechanisms such as staking and masternodes to allow token holders to earn passive income. By staking their tokens or running a masternode, holders contribute to the security and validation of the blockchain network while being rewarded with additional tokens or transaction fees.
In addition to financial rewards, token holders may also receive governance rights. With these rights, holders can participate in the decision-making process of the blockchain project, including voting on important issues and proposing changes to the protocol. This gives token holders a sense of ownership and control over the direction of the project, further incentivizing them to hold and actively engage with their tokens.
Furthermore, some projects offer exclusive benefits or access to token holders. For example, holders may receive discounts on platform fees, early access to new features or products, or priority when participating in token sales or airdrops. These additional benefits create a sense of exclusivity and enhance the value proposition of holding the token, attracting more participants and increasing demand.
Lastly, fostering a strong community is critical for the success of any blockchain project. To incentivize community engagement, token holders may be rewarded for participating in activities such as bug bounties, community discussions, or social media campaigns. By actively engaging with the community, holders contribute to the promotion and development of the project, leading to increased adoption and value of the token.
In conclusion, the economic incentives for token holders are essential in fostering a thriving blockchain ecosystem. By offering financial rewards, governance rights, exclusive benefits, and community participation incentives, projects can motivate holders to actively engage with their tokens, ultimately resulting in the growth and success of the project.
Token Distribution and Economic Equality
Token Distribution:
Token distribution plays a crucial role in determining the level of economic equality within a blockchain network. When tokens are distributed in a fair and equitable manner, it ensures that all participants have an equal opportunity to earn and own tokens.
In the case of Blur, token distribution is done through a decentralized mechanism where users can earn tokens by providing computing power to the network. This approach ensures that token ownership is not concentrated in the hands of a few wealthy individuals or organizations.
This distributed token distribution mechanism helps to create a more egalitarian economic system, where individuals and smaller entities have a fair chance to participate and benefit from the network. It promotes economic inclusion, allowing individuals with limited resources to gain access to tokens and participate in the network's growth.
Economic Equality:
Economic equality is a key consideration in the design and implementation of blockchain networks. By ensuring a fair and equitable distribution of tokens, blockchain networks can help to reduce wealth disparities and promote a more balanced economic system.
When tokens are distributed in a way that is accessible to individuals from diverse economic backgrounds, it creates a level playing field for all participants. This, in turn, fosters a more inclusive and diverse network, where different perspectives and ideas can contribute to the overall growth and development.
Moreover, a more economically equal network also helps to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few, which can lead to unfair practices and manipulation. By promoting economic equality, tokens in the Blur network can be a means of empowering individuals and communities, enabling them to take control of their own economic destiny.
In conclusion, token distribution and economic equality are intrinsically linked in the context of blockchain networks. By ensuring a fair and inclusive token distribution mechanism, blockchain networks like Blur can contribute to the promotion of economic equality, empowering individuals and fostering a more inclusive and balanced economic system.
Economic Impact of Token Distribution Models
The token distribution model employed by a blockchain project can have significant economic implications. This model determines how tokens are allocated and distributed among various stakeholders, including investors, founders, team members, and the wider community. The distribution model can impact the supply and demand dynamics of tokens, as well as the overall economic viability of the project.
There are several different token distribution models that projects can adopt, each with its own potential benefits and drawbacks:
Initial Coin Offering (ICO): This is a popular distribution model where tokens are sold to investors in exchange for another cryptocurrency, typically Bitcoin or Ethereum. ICOs provide a way for projects to raise funds, but they can also lead to a concentration of tokens among a small group of early investors.
Airdrops: In this model, tokens are distributed for free to selected addresses or to the entire community. Airdrops can help to increase token adoption and create a widespread user base, but they can also dilute the value of tokens if they are distributed in large quantities.
Bounties: Projects can allocate tokens as rewards for specific actions or contributions to the project. This can incentivize community participation and engagement, but it may not provide a sustainable long-term distribution model.
Vesting: Some projects opt for a vesting schedule, where tokens are gradually released over a specified period of time. This can ensure that team members and founders have a long-term commitment to the project, but it can also restrict liquidity and limit token availability on the market.
The choice of token distribution model can impact the initial supply of tokens and the level of decentralization within the network. It can also influence the token price, as well as the overall market perception and investor sentiment. Projects need to carefully consider these economic factors when planning their token distribution strategy, taking into account the desired level of community participation, the need for fundraising, and the potential long-term implications for token holders.
In summary, the token distribution model chosen by a blockchain project can have wide-ranging economic effects. It can impact the token supply, demand, liquidity, and market perception. By carefully considering the economic implications of different distribution models, projects can set themselves up for success and foster a healthy ecosystem around their tokens.
Tokenomics and Market Liquidity

The tokenomics of a cryptocurrency project play a crucial role in determining its market liquidity. Market liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. In the case of a cryptocurrency, market liquidity is essential for the smooth functioning of the ecosystem and the viability of the token.
Factors Influencing Market Liquidity
Several factors influence the market liquidity of a cryptocurrency token:
Supply and Demand: The relationship between token supply and demand has a profound impact on market liquidity. If the demand for a token is high and the supply is limited, the token's price is likely to increase, and liquidity may decrease.
Exchanges and Trading Volume: The number and quality of exchanges where a token is listed, as well as the trading volume on these exchanges, directly impact market liquidity. Tokens listed on popular exchanges with high trading volume are generally more liquid.
Market Maker Programs: Market maker programs can enhance market liquidity by incentivizing participants to provide liquidity by placing buy and sell orders. These programs help ensure that there is always someone willing to buy or sell the token, improving overall market liquidity.
Economic Incentives: Tokenomics can include economic incentives to encourage token holders to engage in activities that enhance market liquidity, such as staking, providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges, or participating in governance processes.
Token Distribution: The initial token distribution has a significant impact on market liquidity. If a large percentage of tokens are held by a small group of individuals or entities, liquidity may be restricted. A more equitable token distribution can lead to better market liquidity.
While these factors are essential for market liquidity, it is essential to strike a balance between liquidity and token value. Excessive liquidity can lead to price volatility and market manipulation, while limited liquidity can deter investors and limit token utility.
Economic Implications of Token Burning
Token burning is a mechanism used in blockchain networks to reduce the circulating supply of tokens. This process involves permanently removing a certain number of tokens from circulation, effectively reducing the total supply and potentially increasing the value of the remaining tokens.
1. Supply and Demand Dynamics
Token burning can have a significant impact on the supply and demand dynamics within a blockchain network. By reducing the total supply of tokens, the scarcity of the remaining tokens increases, which can drive up their value. This increased demand, coupled with a reduced supply, can potentially lead to price appreciation.
However, the effect of token burning on the value of tokens is not always straightforward. It depends on various factors such as the magnitude of the burning, the overall market sentiment, and the utility of the tokens in the network. An excessive or uncontrolled burning may disrupt the balance between supply and demand, leading to market volatility and potentially affecting the long-term sustainability of the network.
2. Community Engagement
Token burning can also have positive implications for community engagement. When tokens are burned, it demonstrates a commitment from the project team to reduce token inflation and protect the interests of token holders. This can enhance the trust and confidence of the community and attract more investors and users to the network.
Furthermore, token burning can align the interests of the project team with those of the token holders. As the team holds a certain portion of the tokens, burning a part of their own holdings demonstrates a shared interest in the success and value appreciation of the remaining tokens.
3. Governance and Voting Power
In some blockchain networks, tokens confer governance and voting power to the holders. Token burning can have implications for the distribution of governance and decision-making power within the network.
Burning tokens can decrease the voting power of the burned tokens, potentially consolidating the decision-making power in the hands of a selected group of token holders. This can be seen as both a positive and a negative effect, depending on the level of decentralization desired within the network.
In conclusion, token burning can have significant economic implications for a blockchain network. It can impact the supply and demand dynamics, community engagement, and governance structure of a network. However, the effects of token burning are not always straightforward and depend on various factors. Proper understanding and careful implementation of token burning mechanisms are crucial for achieving the desired outcomes and maintaining a sustainable ecosystem.
Token Distribution and Price Stability

In the world of cryptocurrency, token distribution plays a crucial role in determining its price stability. The way tokens are distributed among holders can have a significant impact on the token's value and the overall health of the market.
Logging into your BLUR.IO account is the first step to gaining access to the token distribution and price stability features. Once logged in, users can understand how tokens are distributed and the factors influencing their price stability.
A fair and balanced token distribution is essential to maintaining price stability. If a large portion of tokens is held by a small number of individuals or entities, it can lead to extreme price volatility. On the other hand, a widespread distribution among a diverse group of holders can help stabilize the token's price.
Token distribution can also be influenced by various economic factors. For example, the initial coin offering (ICO) phase may distribute a significant number of tokens to early investors, which can impact the supply and demand dynamics. Additionally, factors such as the token's utility, scarcity, and market demand can affect its distribution among users.
To ensure price stability, projects often implement mechanisms such as token locks or vesting schedules. These mechanisms prevent early investors from selling off their tokens in large quantities, which can disrupt the market. By gradually releasing tokens into circulation, projects can maintain a more stable and healthy price trajectory.
In summary, token distribution plays a vital role in determining the price stability of a cryptocurrency. A fair and balanced distribution among a diverse group of holders is key to avoiding extreme price volatility. Additionally, implementing mechanisms like token locks can further support price stability. By understanding the economic factors influencing token distribution, users can make informed decisions about their investments and participate in a healthier crypto market.
Economic Factors and Token Governance

When it comes to the distribution and supply of tokens in the blur ecosystem, several economic factors come into play. These factors shape the overall governance of the token and determine how it functions within the ecosystem. Understanding these economic factors is crucial for both users and developers to make informed decisions and maintain a healthy token economy.
Supply and Demand: The law of supply and demand is a fundamental economic principle that applies to token governance as well. The distribution of tokens and the overall token supply directly impact the demand and value of the token. If the token supply is limited and there is high demand, the value of the token is likely to increase. On the other hand, an oversupply of tokens may lead to a decrease in value.
Inflation and Deflation: Inflation and deflation are two economic concepts that affect the token economy. Inflation occurs when the token supply increases, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of the token. Deflation, on the other hand, happens when the token supply decreases, resulting in an increase in token value. Balancing the token supply to maintain a stable economy is crucial for effective token governance.
Token Distribution: How tokens are distributed initially can have a significant impact on the overall token economy. Fair distribution ensures that a wide range of participants have access to tokens, preventing concentration of power and promoting decentralization. Different distribution mechanisms, such as airdrops, token sales, or token mining, can be employed to distribute tokens equitably.
Token Utility: The utility of a token and its use cases play a vital role in token governance. Tokens that have a clear and valuable function within the ecosystem are more likely to attract users and maintain demand. Developers must ensure that the token has a well-defined purpose and actively work to create a thriving ecosystem that encourages token usage.
Community Participation: The involvement of the community in token governance is crucial for its success. Community members should have a say in important decisions, such as token distribution models, inflation/deflation mechanisms, and changes to token utility. This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and ensures that the token ecosystem evolves in a way that benefits all stakeholders.
By considering these economic factors and implementing effective token governance, developers can create a sustainable and thriving token economy within the blur ecosystem. This will not only attract users and investors but also contribute to the long-term success of the project.
Token Distribution and Market Speculation
Token distribution in the blur ecosystem plays a crucial role in influencing market speculation. The distribution of tokens determines the initial availability and scarcity of the assets, influencing their perceived value and potential future adoption.
The initial token distribution is often done through a token sale or initial coin offering (ICO). During this process, a certain percentage of the total token supply is allocated to investors, early supporters, team members, and other participants. The distribution strategy can vary, with some projects opting for a more fair and decentralized approach while others may concentrate a significant portion of tokens in the hands of a few key stakeholders.
When token distribution is heavily skewed towards a few individuals or entities, it can lead to market speculation and volatility. The concentration of tokens in the hands of a small group can create a situation where the actions and decisions of these stakeholders have a significant impact on the market. This can lead to price manipulation, insider trading, and other market manipulation practices.
On the other hand, a more decentralized and widespread token distribution can help minimize market speculation and volatility. When tokens are distributed among a larger number of participants, it becomes harder for any single entity to influence the market significantly. This can promote a healthier and more stable market environment, attracting more diverse stakeholders and encouraging wider adoption of the token.
In addition to the initial token distribution, ongoing token supply and liquidity management also play a role in market speculation. If a project has a limited token supply, it can create a situation where demand for the tokens exceeds their availability, leading to a rise in their value. This can further fuel market speculation and create a FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out) effect among investors.
Moreover, the release of additional tokens into the market can also impact market speculation. Projects that have a structured and transparent token release schedule can help manage market expectations and minimize sudden price fluctuations. Conversely, sudden and large token releases can lead to market uncertainty and volatility, as investors may perceive the increased supply as a potential devaluation of the tokens.
In conclusion, token distribution and supply management are key factors influencing market speculation. A fair and decentralized distribution approach, combined with transparent and predictable token releases, can foster a more stable market environment and encourage wider adoption of tokens.
Economic Factors Affecting Token Utility
Token utility plays a crucial role in determining the value and demand of a token within the Blur ecosystem. Several economic factors influence the utility of a token, including:
1. Supply and Demand:
The supply and demand dynamics of a token have a direct impact on its utility. If the supply of a token is limited while the demand is high, the token's value and utility are likely to increase. On the other hand, if the supply of a token exceeds the demand, its utility may decrease.
2. Token Distribution:
The distribution of tokens among various stakeholders also affects their utility. If the token distribution is concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or entities, it may lead to centralization and reduce the token's utility. Conversely, a more decentralized distribution can enhance the token's utility and promote wider adoption.
3. Governance and Voting Rights:
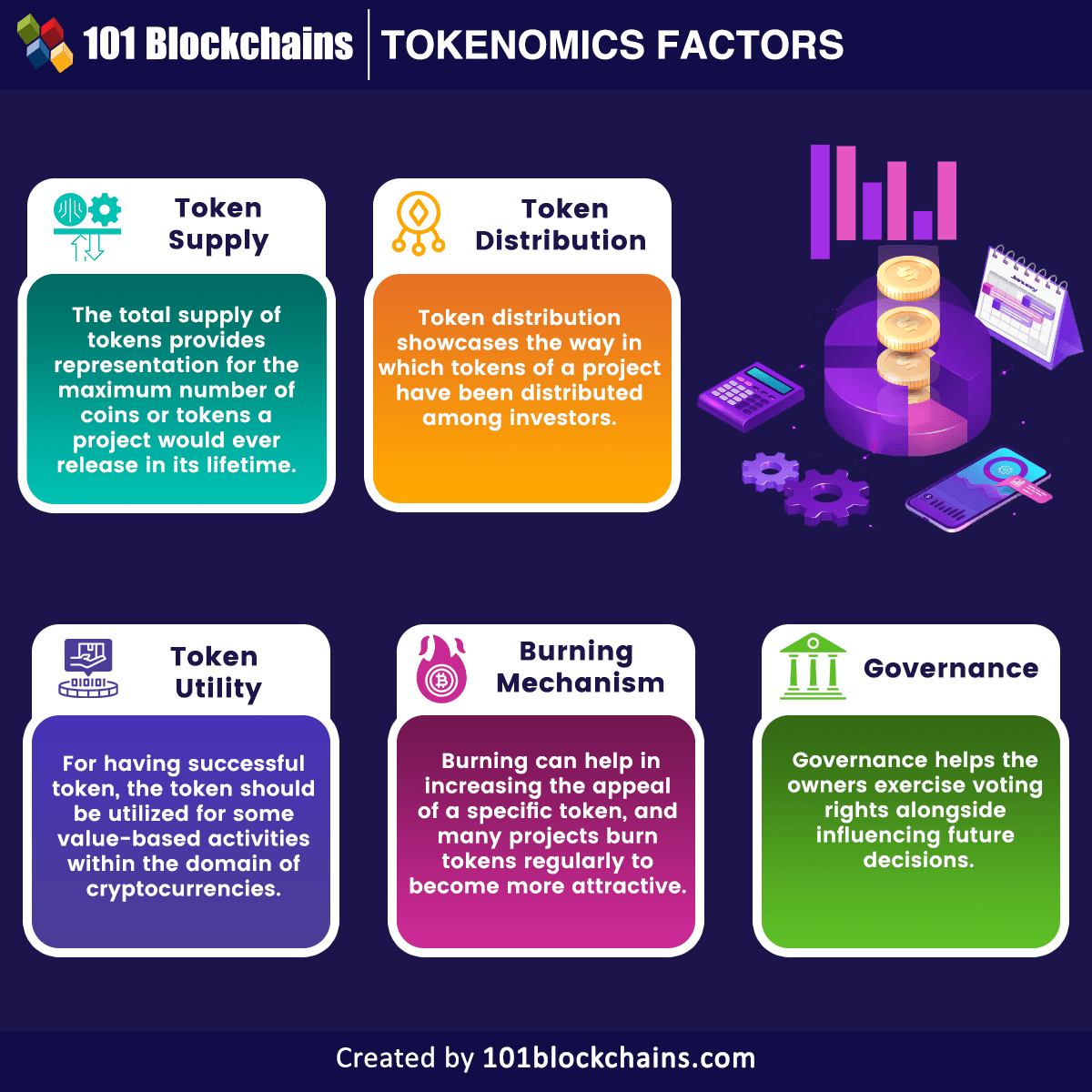
Some tokens provide holders with governance and voting rights within the ecosystem. Tokens with such features are likely to have higher utility, as they allow holders to actively participate in decision-making processes and influence the direction of the platform.
4. Staking and Rewards:
Tokens that offer staking and rewards mechanisms can also have increased utility. Staking allows token holders to lock their tokens in a smart contract and receive rewards in return. This incentivizes holding the token and allows holders to generate additional income, increasing its utility.
5. Use Case and Functionality:
The use case and functionality of a token play a crucial role in its utility. Tokens that are integral to the core operations of a platform or have multiple use cases are likely to have higher utility. Additionally, if the token can be used for various services or products within the ecosystem, it enhances its value and utility.
Supply and Demand
The balance between token supply and the demand within the market.
Token Distribution
The way tokens are distributed among holders and stakeholders.
Governance and Voting Rights
Tokens that provide holders with governance and decision-making powers.
Staking and Rewards
Token holders are able to stake their tokens and earn rewards.
Use Case and Functionality
Tokens that have specific use cases and functionality within the ecosystem.
What are the economic factors that influence token distribution and supply in blur?
The economic factors that influence token distribution and supply in blur can vary, but some common factors include market demand, token issuance mechanisms, and economic incentives for token holders.
How does market demand affect token distribution and supply in blur?
Market demand plays a crucial role in determining token distribution and supply in blur. If there is high demand for the token, it may lead to a higher distribution rate as more people want to acquire the token. On the other hand, if market demand is low, the distribution and supply may be limited to prevent oversupply and ensure the token retains its value.
What are token issuance mechanisms and how do they influence token distribution and supply in blur?
Token issuance mechanisms refer to the methods through which tokens are created and distributed. The specific mechanism used can greatly impact token distribution and supply in blur. For example, if tokens are minted and distributed regularly, it may result in a higher token supply. Conversely, if tokens are distributed through a limited supply mechanism such as an initial coin offering (ICO) or a token sale, it can create scarcity and influence token value.
Are there any economic incentives for token holders in blur?
Yes, there are often economic incentives for token holders in blur. These incentives can include rewards for holding tokens, such as staking rewards or participation in governance processes. By providing economic incentives, projects aim to encourage token holders to actively participate in the ecosystem and contribute to its growth.
How do economic factors affect the token distribution and supply in blur?
Economic factors have a direct impact on token distribution and supply in blur. Factors such as market demand, token issuance mechanisms, and economic incentives can determine the rate at which tokens are distributed, the total token supply, and the value of the token. By carefully considering these factors, projects can optimize token distribution and supply to create a healthy and sustainable ecosystem.
Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto
2022-2024 @ An exploration of the economic factors influencing token distribution and supply in blur