Exploring the Role of Blockchain in Ensuring Trust and Security for NFT Storage
Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto
Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto
In the world of digital assets, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have become a game-changer. These unique tokens have revolutionized the way we perceive and value digital art, collectibles, and even virtual real estate. But one question remains: how can we ensure the trustworthiness and security of these valuable digital assets? The answer lies in the blockchain technology.
Blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, plays a vital role in guaranteeing the trust and security of NFT storage. Each NFT is uniquely identified and verified through a cryptographic hash stored on the blockchain. This immutable record of ownership ensures that the NFT cannot be tampered with or counterfeited.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority to oversee and regulate NFT transactions. Instead, the validation and verification of these transactions are carried out by a network of computers, known as nodes, spread around the world. This distributed consensus mechanism makes it extremely difficult for any malicious actor to manipulate the blockchain and compromise the integrity of NFT storage.
Additionally, smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, play a crucial role in ensuring the security of NFT storage. These contracts, built on top of blockchain platforms like Ethereum, automatically enforce the rules and conditions associated with the ownership and transfer of NFTs. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of fraud or disputes.
In conclusion, the blockchain technology provides a robust and trustworthy foundation for NFT storage. Through its decentralized and immutable nature, coupled with the use of smart contracts, the blockchain ensures the integrity, security, and irrefutable ownership of NFTs. As the popularity of NFTs continues to soar, understanding the underlying blockchain technology becomes essential for artists, collectors, and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger technology that allows multiple parties to reach consensus on the state of a shared database without the need for a trusted central authority. It was first introduced through the invention of Bitcoin by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
How Does Blockchain Work?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and transparent digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Each transaction, or block, is linked to the previous one through a cryptographic hash function, creating a chain of blocks. This chain is stored and replicated across the network of computers, known as nodes, that participate in the blockchain network.
When a new transaction is proposed, it is broadcasted to all the nodes in the network. The nodes then validate the transaction using a consensus algorithm, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, to ensure its validity. Once the transaction is validated, it is added to a new block, which is then added to the existing chain of blocks, creating an immutable record of all transactions.
Key Features of Blockchain
There are several key features that make blockchain technology unique and revolutionize trust and security:
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for a central authority or intermediary. This reduces the risk of single points of failure and makes it resistant to censorship and control by any single entity.
Transparency: All transactions recorded on the blockchain are transparent and can be viewed by anyone with access to the network. This enhances accountability and trust among participants.
Security: Blockchain utilizes advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions. Each block is linked to the previous one through a hash function, making it virtually impossible to alter or tamper with past transactions without the consensus of the network.
Immutability: Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unchangeable part of the ledger. This ensures the integrity of the data and prevents fraudulent activities.
Smart Contracts: Blockchain can support the execution of self-executing contracts known as smart contracts. These contracts automatically enforce the terms and conditions set within them, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and verify transactions. Its use cases extend beyond cryptocurrencies and can be applied to supply chains, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and more.
Exploring the Key Concepts of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we store and exchange information, ensuring trust and security in various applications. One of the key concepts of the blockchain is its decentralized nature, where data is not stored in a central authority or server, but rather distributed across a network of computers, called nodes. This distributed nature of the blockchain ensures that no single entity can control or manipulate the data, making it highly resistant to tampering and fraud.
Another important concept of blockchain is immutability. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to change or delete it. This is achieved through cryptographic algorithms that link each block of data to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name "blockchain". Any attempt to alter a block would require changing the subsequent blocks as well, which would be computationally infeasible due to the decentralized and distributed nature of the blockchain network.
Blockchain also embraces transparency, allowing all participants to view and verify the stored data. This transparency is achieved through a consensus mechanism, where multiple nodes in the network validate and agree on the accuracy of the data before it is added to the blockchain. Once added, the data becomes publicly accessible and can be audited by anyone, ensuring accountability and eliminating the need for intermediaries or trusted third parties.
Blockchain Technology and its Applications
Blockchain technology, originally introduced as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has gained significant attention and recognition due to its potential applications in various industries. The core concept behind blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that keeps a record of transactions and ensures security, transparency, and trust.
Security and Trust
One of the primary advantages of blockchain technology is its robust security features. Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers known as nodes, which work together to validate and record transactions. Each transaction is securely encrypted and linked to the preceding transaction through a cryptographic hash, forming a chain of blocks. This makes it extremely difficult for hackers to alter or tamper with any transaction data, ensuring the integrity and immutability of the information stored on the blockchain.
Moreover, blockchain technology uses consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), that require participants in the network to solve complex mathematical problems or hold a certain amount of digital assets to validate transactions. This consensus mechanism further enhances security and prevents malicious activities, as it would require an attacker to control a majority of the nodes in the network, which is highly impractical and costly.
By offering enhanced security features and eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain technology provides a high level of trust in the storage and transfer of assets or information. This makes it particularly useful in applications where trust is crucial, such as financial transactions, supply chain management, and digital identity verification.
Applications in Various Industries
The potential applications of blockchain technology go beyond cryptocurrencies. Industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and even arts and entertainment are exploring how blockchain can revolutionize their operations and improve efficiency.
In the financial sector, blockchain technology has the potential to streamline and automate processes, reduce costs, and increase transparency. The use of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can eliminate the need for intermediaries and ensure secure and transparent transactions.
In healthcare, blockchain technology can improve data security and interoperability, making it easier for different healthcare providers to access and share patient records securely. Additionally, blockchain can facilitate the tracking and verification of the authenticity of drugs and medical devices, reducing the risk of counterfeit products entering the supply chain.
The art industry has also embraced blockchain technology, particularly in the form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs allow artists to represent ownership and authenticity of digital artwork, collectibles, and other unique digital assets. By utilizing blockchain technology, artists can have greater control over their work, prevent unauthorized duplication, and ensure the provenance of their creations.
Overall, blockchain technology holds immense potential for transforming various industries by providing enhanced security, transparency, and trust. As the technology continues to evolve and overcome scalability challenges, we can expect to see increased adoption and innovative applications in the future.
Exploring the Trust Mechanism of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we perceive trust and security in digital transactions. In traditional systems, trust is established through intermediaries such as banks, governments, or other centralized authorities. However, the blockchain introduces a decentralized trust mechanism that removes the need for intermediaries and ensures transparency, immutability, and security.
At the core of the blockchain's trust mechanism is its distributed ledger, which consists of blocks of information that are linked together using cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a list of transactions and a reference to the previous block, forming a chain of blocks. This structure ensures that every transaction is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a tamper-evident record that cannot be altered without detection.
To validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain, a consensus mechanism is employed. Different blockchain networks use various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These algorithms ensure that multiple participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain.
Another crucial aspect of the blockchain's trust mechanism is its decentralized nature. Instead of relying on a single central authority, the blockchain leverages a network of nodes, each storing a copy of the entire blockchain. This decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the blockchain, making it resistant to censorship and single points of failure.
Furthermore, the immutability of the blockchain enhances trust by preventing data tampering. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete it. This feature provides an auditable and transparent record of all transactions, making the blockchain suitable for applications where trust and accountability are paramount.
Transparency
The blockchain provides transparency by allowing anyone to view the entire transaction history.
Security
The cryptographic nature of the blockchain ensures that transactions are secure and tamper-evident.
Decentralization
The decentralized nature of the blockchain prevents a single point of failure and eliminates the need for intermediaries.
Immutability
Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring a reliable record of transactions.
In conclusion, the trust mechanism of the blockchain rests on its distributed ledger, consensus algorithms, decentralization, and immutability. These features work together to create a transparent, secure, and trustworthy system for digital transactions.
Understanding the Role of Cryptography in Blockchain
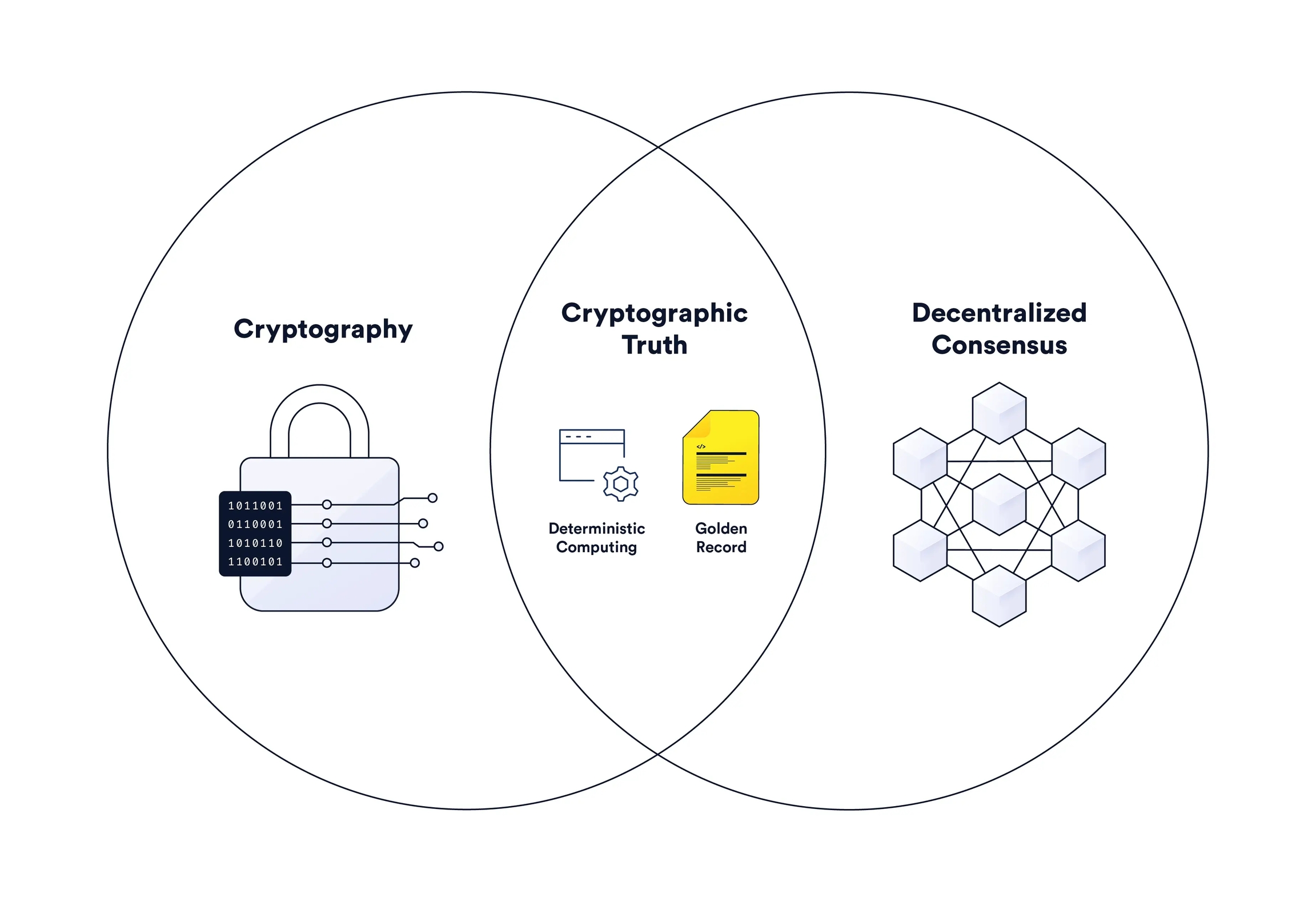
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the trust and security of blockchain technology. By leveraging various cryptographic techniques, blockchain systems are designed to secure digital assets and transactions. Here are some key aspects of cryptography in blockchain:
Secure Transactions: Cryptography provides a method for securely transmitting and verifying transactions on the blockchain network. Every transaction is encrypted using public-key cryptography, making it almost impossible for unauthorized parties to tamper with or forge transactions.
Privacy and Anonymity: Cryptography allows blockchain users to maintain a certain level of privacy and anonymity. By using public-key cryptography, users can generate unique addresses that represent their identities without revealing personal information. This way, transactions can be traced and verified without compromising users' privacy.
Digital Signatures: Cryptography enables users to confirm the authenticity and integrity of data stored on the blockchain through digital signatures. Digital signatures are generated using public and private key pairs, ensuring that the data has not been altered or tampered with since it was signed.
Encryption: Cryptography is also used to encrypt sensitive data stored on the blockchain, such as personal information or confidential documents. By encrypting data, it becomes extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to access or decrypt the information without the corresponding decryption keys.
Consensus Mechanisms: Cryptographic algorithms are a fundamental component of consensus mechanisms in blockchain systems. Consensus mechanisms ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. This is achieved through cryptographic puzzles and algorithms that require computational effort to solve, preventing malicious actors from gaining control of the network.
Immutable Recordkeeping: Cryptography plays a vital role in maintaining the immutability of blockchain records. By using hash functions, each block in the blockchain is linked to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks. Cryptographic hashes ensure that any modification to a block would result in a completely different hash, thus rendering the entire chain invalid.
In conclusion, cryptography is a fundamental element of blockchain technology, providing the necessary tools to ensure the trust, security, and integrity of digital assets and transactions. Without cryptography, the decentralization and transparency that blockchain offers would not be possible.
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Networks
In blockchain networks, consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and trust of the network. Consensus mechanisms are algorithms or protocols that enable the participants of a blockchain network to agree on the state of the network and validate new transactions.
One of the most commonly used consensus mechanisms in blockchain networks is Proof of Work (PoW). In a PoW consensus mechanism, participants, known as miners, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate new blocks of transactions. The miner who successfully solves the puzzle first is rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency. This mechanism ensures that the participants in the network invest computational power and resources to validate transactions, making it difficult for malicious actors to gain control of the network.
Another popular consensus mechanism is Proof of Stake (PoS). In a PoS consensus mechanism, participants called validators are chosen to validate new blocks based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral. Validators are selected randomly, with the probability of being chosen proportional to the number of tokens they hold. Validators who propose invalid blocks or try to cheat the system can have their staked tokens confiscated. PoS is considered to be more energy-efficient than PoW as it does not require extensive computational power.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a variation of the PoS consensus mechanism that introduces a voting system. Token holders in the network can vote for a set of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the blockchain. These delegates are given the power to produce blocks and are rewarded for their services. DPoS ensures decentralization while allowing token holders to have a say in the governance of the network.
Proof of Authority (PoA) is a consensus mechanism that relies on a set of trusted validators rather than computational power or stake. Validators are pre-selected and are known entities that have a reputation to uphold. PoA can provide faster transaction confirmation times compared to PoW or PoS, but it sacrifices some level of decentralization and trustlessness.
Overall, consensus mechanisms are essential for maintaining the security and trust of blockchain networks. Different mechanisms have their own advantages and trade-offs, and their selection depends on the specific requirements and goals of the network.
Examining the Immutability of Blockchain

One of the key features that makes blockchain technology highly secure is its immutability. Immutability refers to the inability to change or alter data once it has been added to the blockchain. This characteristic provides a robust and trustless system for storing and verifying information.
Blockchain achieves immutability through cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms. When a new block is added to the chain, it is linked to the previous block through hashing. Hashing is a process of converting data into a fixed-size string of characters, which is unique to that data. This cryptographic link creates a chain of blocks, where each block contains a reference to the previous block's hash.
In order to alter any data within a block, one would need to modify not only the hash of that particular block but also the hashes of all subsequent blocks. This is an extremely difficult task due to the computational power required and the distributed nature of the blockchain network. Additionally, each block includes a timestamp, further adding to the immutability of the data.
The consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks, such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), further enhances the immutability of the system. These mechanisms require participants to solve complex mathematical problems or stake their own tokens as collateral to validate and add new blocks to the chain. Consensus ensures that a majority of participants within the network agree on the validity of the transactions, making it nearly impossible to manipulate the data retroactively.
The immutability of blockchain technology is particularly important for storing and securing NFTs (non-fungible tokens). NFTs represent unique digital assets, such as artwork or collectibles, and their value heavily relies on the assurance that they cannot be tampered with. The decentralized nature and immutability of blockchain provide a level of trust and security that traditional centralized systems cannot match.
1. Trustless system for data storage
1. Difficulty in correcting erroneous data
2. Protection against data tampering and fraud
2. Potential accumulation of outdated or irrelevant information
3. Enhanced security for sensitive information
3. Need for appropriate mechanisms to handle disputes or errors
In conclusion, the immutability of blockchain technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the trust and security of data storage, not only for NFTs but also for various other applications. Through cryptographic algorithms, hashing, and consensus mechanisms, the blockchain creates an unchangeable and decentralized ledger, which makes it an ideal solution for storing valuable digital assets.
Decentralization and its Impact on Trust in Blockchain
In the world of blockchain technology, decentralization plays a crucial role in establishing trust and security. Unlike traditional systems that rely on a central authority, blockchain operates on a distributed network of computers called nodes. Each node in the network holds a complete copy of the blockchain database, making it impossible for a single point of failure or manipulation.
This decentralized nature of blockchain ensures transparency and immutability. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is verified and stored in multiple copies across different nodes. This redundancy eliminates the risk of data loss or tampering, as altering a single copy would require hacking into each and every participating node.
In addition to the security aspect, decentralization also enhances trust in blockchain technology. With a centralized system, users have to place their trust in a single entity that controls and manages the database. This central authority can potentially abuse its powers and compromise the integrity of the data. However, in a decentralized blockchain, trust is distributed among the network participants. No single entity has complete control over the system, making it more resistant to corruption and censorship.
Furthermore, decentralization fosters trust by enabling transparent governance. Major blockchain networks are operated and governed by consensus mechanisms, often involving multiple stakeholders. This inclusive decision-making process ensures that the interests of all participants are taken into account, reducing the chances of biased actions or unfair practices.
In summary, decentralization is a fundamental principle that underpins the trust and security provided by blockchain technology. By eliminating central authorities and empowering a distributed network of nodes, blockchain creates a transparent, tamper-resistant, and trustworthy environment for storage and management of NFTs.
Ensuring Security in Blockchain Networks
In the world of digital assets, security is paramount. Blockchain networks provide a robust and secure foundation for storing and transacting non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Here are some key principles that ensure the security of blockchain networks:
1. Distributed Ledger
Blockchain operates on a distributed ledger system, where all participants in a network have a copy of the same ledger. This shared ledger eliminates the need for a central authority or intermediary, making it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate or tamper with transactions.
2. Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate and confirm transactions. These mechanisms ensure that the majority of participants agree on the validity of the transaction, preventing double-spending and other fraudulent activities.
3. Cryptographic Security
Blockchain networks rely on cryptography to secure transactions and identities. Each transaction is cryptographically signed to ensure its integrity and authenticity. Additionally, public-key cryptography is used to verify the ownership and transfer of NFTs, providing a high level of security.
4. Immutable and Transparent Records

Once a transaction is added to a blockchain, it becomes immutable and cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures the integrity of the records and provides a transparent audit trail for any transaction or asset stored on the blockchain. This transparency enhances trust in the network.
5. Smart Contracts

Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded on the blockchain. They enable automated and secure transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts ensure that the agreed-upon terms are met before executing any transaction, enhancing security and trust.
By leveraging these security measures, blockchain networks provide a robust and trusted environment for storing and transacting NFTs. Whether you are an artist, collector, or investor, understanding the security features of blockchain networks is essential to protect your digital assets.
For more information on blockchain network security, you can Se connecter à Blur.io: Explorer les caractéristiques et les avantages de Blur.io. Blur.io provides detailed insights into the security features and advantages of blockchain networks for NFT storage.
Securing Transactions with Blockchain Technology
When it comes to digital transactions, security and trust are of utmost importance. Traditional systems rely on intermediaries and central authorities to facilitate transactions, which can introduce vulnerabilities and potential points of failure. However, blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure solution for securing transactions, which is especially relevant in the context of NFT storage.
Blockchain technology operates on a distributed ledger system, where transactions are recorded across multiple nodes or computers. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority and ensures that no single entity can manipulate or control the transaction data. Each transaction is verified and recorded in a transparent and immutable manner, providing a high level of security and trust.
How Blockchain Guarantees Trust
One of the key mechanisms that ensures trust in blockchain transactions is the consensus algorithm. This algorithm requires a majority of participants, known as nodes, to agree on the validity of a transaction before it is added to the blockchain. This eliminates the risk of fraudulent or double-spending transactions, as any malicious activity would require the collusion of the majority of nodes.
In addition to consensus, blockchain technology also employs cryptography to secure transactions. Each transaction is digitally signed using cryptographic algorithms, which ensures the authenticity and integrity of the data. This cryptographic signature serves as proof that the transaction has not been tampered with, providing an additional layer of security.
Securing NFT Storage
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, have gained significant popularity in recent years. These unique digital assets represent ownership of a particular item or piece of content, such as artwork or music. The secure storage of NFTs is crucial to prevent theft or unauthorized duplication.
Blockchain technology provides a secure and transparent solution for NFT storage. By leveraging blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature, NFTs can be securely stored and transferred. Each NFT is associated with a specific smart contract on the blockchain, which defines its ownership and ensures its uniqueness. The transparent nature of the blockchain allows anyone to verify the authenticity and ownership of an NFT, further enhancing trust in the ecosystem.
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers a robust solution for securing transactions, especially in the context of NFT storage. By leveraging decentralization, consensus algorithms, and cryptography, blockchain ensures trust and security in digital transactions. The secure storage of NFTs on the blockchain further strengthens the integrity and uniqueness of these digital assets. As blockchain technology continues to advance, it holds the potential to revolutionize various industries and redefine how we transact and store digital assets.
Understanding the Role of Smart Contracts in Blockchain Security
In the world of blockchain technology, security is of utmost importance. As a decentralized and open network, the blockchain ensures trust and security through various mechanisms, one of which is smart contracts.
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute when the predefined conditions are met. These contracts are stored on the blockchain, making them immutable and transparent to all participants.
Smart contracts play a crucial role in blockchain security as they eliminate the need for intermediaries and provide a decentralized platform for executing transactions. By removing intermediaries, smart contracts reduce the risks of fraud and tampering.
Enhancing Security through Automation
The programmable nature of smart contracts enables the automation of various processes, enhancing the security of blockchain networks. Through smart contracts, transactions can be executed automatically, ensuring that all parties involved adhere to the predefined terms.
This automation eliminates human error and reduces the potential for malicious activities, as the execution of transactions is determined solely by the code within the smart contract. This makes the blockchain network more robust and secure, as it removes the possibility of human manipulation.
Immutable and Transparent Execution
Smart contracts are stored on the blockchain, which provides an immutable and transparent execution environment. Once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered, deleted, or tampered with unless specific conditions written in the contract allow for such changes.
This immutability ensures that the terms of the contract remain unchanged and resistant to external influences. Additionally, the transparent nature of the blockchain allows all participants to view and verify the execution of smart contracts, ensuring trust and reducing the risks of fraud.
In conclusion, smart contracts are integral to the security of blockchain networks. By automating processes, eliminating intermediaries, and providing an immutable and transparent execution environment, smart contracts enhance the trust and security of blockchain technology, making it a reliable platform for storing and transacting with NFTs.
The Role of Blockchain in NFT Storage
The emergence of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) has presented a new way of owning and transferring digital assets. However, the question of trust and security is still paramount. This is where blockchain technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and provenance of NFT storage.
Blockchain, the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, is a decentralized and immutable ledger. It provides a tamper-proof record of transactions and ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be modified or tampered with.
When it comes to NFT storage, blockchain acts as a secure and transparent way to store digital assets. Each NFT is represented by a unique token, and its ownership and transaction history are recorded on the blockchain. This means that anyone can verify the authenticity and ownership of an NFT by simply checking the blockchain records.
Furthermore, blockchain technology allows for the transfer of ownership without the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enable seamless and trustless transactions. Once the conditions of a smart contract are met, ownership of the NFT is automatically transferred, eliminating the need for third-party involvement.
The decentralized nature of blockchain also ensures that NFT storage is resistant to censorship and control. Unlike centralized servers or platforms that can be shut down or manipulated, blockchain-based NFT storage is distributed across a network of computers. This means that even if one node goes offline, the data is still accessible from other nodes, ensuring the continuity and availability of the stored NFTs.
Overall, blockchain plays a vital role in guaranteeing trust and security for NFT storage. Its immutable nature, transparent records, and decentralized architecture provide a reliable and tamper-proof solution. With the increasing popularity of NFTs, the role of blockchain in ensuring the integrity of digital assets will continue to be of utmost importance.
Exploring the Benefits of Blockchain for NFT Storage

The rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has brought about a new era in digital ownership and the way we store valuable assets. With traditional forms of storage, such as centralized servers or physical mediums, there is always a risk of loss, fraud, or manipulation. However, blockchain technology offers a revolutionary solution to these concerns.
One of the key benefits of using blockchain for NFT storage is the inherent security it provides. Every transaction and ownership of an NFT is recorded on a decentralized ledger, known as the blockchain. This means that once an NFT is minted and stored on the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to modify, tamper with, or forge.
This immutability ensures that the integrity of the NFT remains intact, creating a transparent and trustworthy digital ecosystem. Unlike centralized storage systems, where the ownership and authenticity of an asset can be disputed, blockchain technology guarantees the provenance and validity of every NFT.
Another advantage of blockchain for NFT storage is the elimination of middlemen and intermediaries. Traditionally, when storing valuable assets, one would need to rely on third-party custodians or storage providers. These intermediaries come with additional costs and may introduce unnecessary risks, such as data breaches or mismanagement of assets.
With blockchain, NFT owners have complete control over their assets, eliminating the need for intermediaries. By using a decentralized storage system, individuals can securely store their NFTs without the risk of relying on a centralized authority.
Furthermore, blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability for NFT storage. Every transaction on the blockchain is publicly recorded, allowing anyone to track the history of an NFT. This feature is particularly beneficial for artists and creators, as it provides a clear record of ownership and helps prevent unauthorized reproductions or counterfeit NFTs.
Additionally, the use of blockchain for NFT storage enables interoperability across different platforms and marketplaces. As NFTs gain popularity, various platforms and marketplaces have emerged, each with its own unique features and advantages.
Thanks to blockchain technology, NFTs can be easily transferred and traded between these platforms, creating a truly global and interconnected marketplace. This interoperability opens up new opportunities for artists, collectors, and investors, allowing them to reach a wider audience and maximize the value of their NFTs.
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers numerous benefits for NFT storage. Its security, immutability, elimination of intermediaries, transparency, and interoperability make it the ideal choice for storing and safeguarding these valuable digital assets. As the NFT space continues to grow, the importance and advantages of blockchain for storage will only become more apparent.
Understanding the Trust and Security Guarantees of Blockchain for NFTs
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we store and transfer various types of digital assets, including non-fungible tokens (NFTs). By leveraging decentralized networks and cryptography, blockchain ensures trust and security in NFT storage and transactions.
Decentralization and Transparency

One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional systems where a central authority controls and verifies transactions, blockchain relies on a network of computers, known as nodes, to validate and record transactions in a distributed and transparent manner.
Every transaction involving NFTs is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable and auditable history. This transparency allows anyone to verify the ownership and authenticity of an NFT, providing a high level of trust.
Immutable and Secure Ledger
Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques, such as hashing and digital signatures, to ensure the immutability and security of the ledger. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the transaction history.
The use of public and private keys further enhances the security of NFT storage. Each NFT is assigned a unique digital signature, which is linked to the owner's private key. Only the owner of the private key can transfer or modify the NFT, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring secure ownership.
Smart Contracts and Programmability
Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements written in code, play a crucial role in the trust and security guarantees of blockchain for NFTs. Smart contracts automatically execute transactions and enforce predefined rules, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud.
By embedding NFT metadata and ownership conditions within smart contracts, blockchain ensures the seamless transfer of NFTs while maintaining trust and security. Smart contracts also enable the creation of unique features, such as royalties and secondary market controls, which further enhance the value and utility of NFTs.
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and transparent solution for NFT storage.
The immutability and security of the blockchain ledger ensure trust in NFT ownership.
Smart contracts automate transactions and enforce predefined rules for secure NFT transfers.
In conclusion, the use of blockchain technology provides robust trust and security guarantees for the storage and transfer of NFTs. By leveraging decentralized networks, cryptography, and smart contracts, blockchain ensures transparency, immutability, and secure ownership of NFTs in a highly programmable and efficient manner.
What is blockchain and how does it guarantee trust and security for NFT storage?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It guarantees trust and security for NFT storage by using cryptographic principles and consensus algorithms to validate and verify each transaction. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable and tamper-proof, ensuring that the ownership and authenticity of NFTs are protected.
Why is trust important in NFT storage?
Trust is important in NFT storage because it ensures that the ownership and authenticity of digital assets are accurately represented. Without trust, there is a risk of fraud and counterfeit NFTs being circulated. By leveraging blockchain technology, which guarantees trust through decentralized verification and consensus mechanisms, NFT storage can provide a secure and reliable way to verify ownership and prevent fraud.
What are the security risks associated with NFT storage?
NFT storage faces several security risks, including hacking, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access to private keys. Hackers can target individuals or platforms that store NFTs and steal valuable digital assets. Phishing attacks can trick users into revealing their private keys or accessing malicious websites. Poorly implemented security measures can also lead to unauthorized access. To mitigate these risks, it is important to use secure wallets, enable two-factor authentication, and be cautious of suspicious links or requests.
How does blockchain prevent tampering with NFTs?
Blockchain prevents tampering with NFTs by using cryptographic algorithms and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Each NFT transaction is digitally signed, creating a unique cryptographic hash that is linked to the previous transaction. These transactions are stored across multiple computers in a network, making it extremely difficult for anyone to tamper with the data without the consensus of the majority. Additionally, the transparency of the blockchain allows users to verify the history and authenticity of NFTs.
Can blockchain technology be hacked?
While blockchain technology is generally considered secure, it is not completely immune to hacking. While the decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult to compromise the entire network, individual users or platforms can still be vulnerable to hacking attempts. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in wallets, private keys, or centralized exchanges to gain unauthorized access or steal digital assets. It is essential for users to follow best security practices, such as using hardware wallets, keeping software up to date, and being cautious of phishing attempts.
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures transparency, security, and trust as each transaction is verified by multiple participants in the network.
How does the blockchain guarantee trust and security for NFT storage?
The blockchain guarantees trust and security for NFT storage through the use of cryptographic algorithms and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Each NFT is assigned a unique digital signature, making it tamper-proof and ensuring authenticity. Additionally, the decentralized nature of the blockchain ensures that no single entity has control over the data, reducing the risk of data manipulation or loss.
What are the benefits of using blockchain for NFT storage?
Using blockchain for NFT storage offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides immutability, meaning that once an NFT is created and added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This helps to ensure the authenticity and provenance of the NFT. Secondly, blockchain provides transparency, allowing anyone to view the transaction history of an NFT and verify its ownership. Lastly, blockchain offers security by using encryption algorithms and decentralized consensus mechanisms to protect the NFT from unauthorized access or tampering.
Blur: NFT | Blur: NFT login | Blur: NFT connect | WalletConnect | Traders | What Is Blur Crypto
2022-2024 @ Understanding how the blockchain guarantees trust and security for nft storage